- Article
Digital Workflows in Broadcast Management
An Introduction to Broadcast Digital Workflows
A digital workflow refers to a series of automated processes that facilitate the flow of information and tasks within a digital environment. Digital workflows in broadcasting industry encompass all aspects of broadcasting, including production, distribution, and the broadcasting itself.
From the initial stages of pre-production, where scripting and planning take shape, to the intricate processes of editing and post-production, digital tools enable teams to collaborate seamlessly and produce high-quality content. Once the content is ready, it moves into the distribution phase, where it is encoded and delivered across various platforms and devices.
Finally, in the broadcasting phase, advanced transmission technologies and real-time monitoring systems guarantee that content is delivered to viewers with optimal quality and engagement. This integration of digital workflows not only streamlines operations but also empowers creators to meet the evolving demands of audiences in a rapidly changing media environment.
Digital Workflow processes
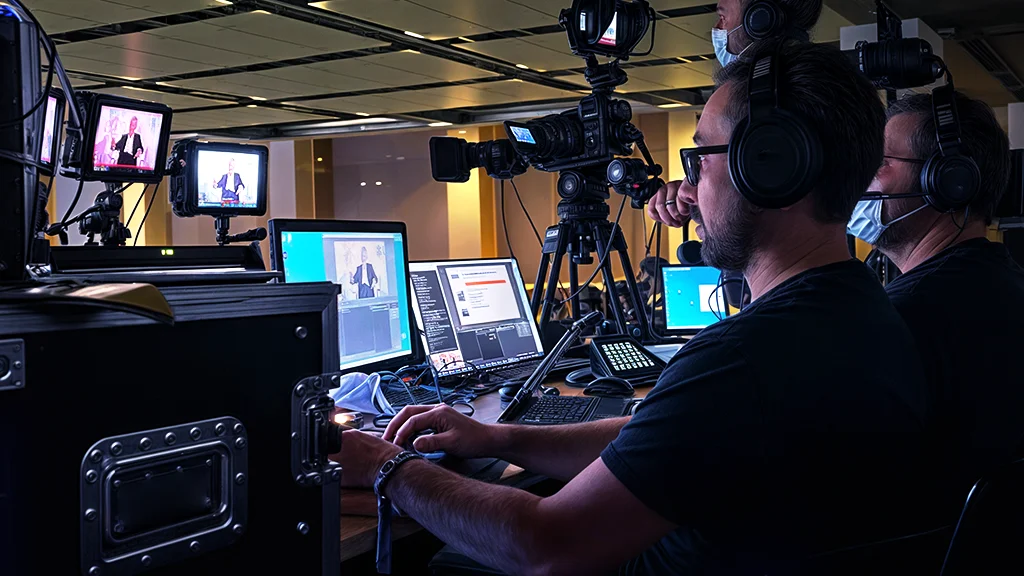
Digital broadcast workflows encompass the end-to-end processes that manage the transmission of content to viewers. These workflows leverage digital technology to streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and improve efficiency. Here’s a breakdown of each stage: production, distribution, and broadcasting.
1. Production
A. Pre-Production
Scripting & Storyboarding: Utilize digital tools for writing scripts and creating storyboards.
Planning & Scheduling: Project management tools help coordinate schedules, budgets, and resources.
Casting & Crew Management: Digital databases and platforms for casting calls and crew recruitment.
B. Production
Shooting: Digital cameras and workflows (such as RAW formats) that allow for higher-quality capture and flexibility in post-production.
Digital Asset Management (DAM): Systems to media asset management (manage video, audio, graphics, and other assets).
Collaboration Tools: Tools for file sharing, and communication platforms for team coordination.
Studio Intercom System: An integrated solution for digital audio messaging and addressing over IP in broadcast production studios for better staff coordination.

C. Post-Production
Editing: Non-Linear Editing (NLE) software enables editing sessions to be collaborative and efficient.
Visual Effects & Graphics: Software for adding visual effects and integrating graphics into the content.
Audio Post-Production: Tools for mixing and mastering audio tracks.
Quality Control: Automated QC tools to ensure content meets broadcasting standards.
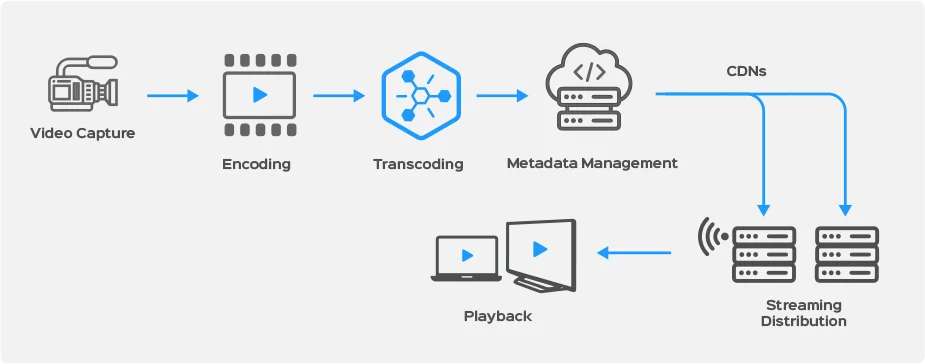
2. Distribution
A. File Transfer
Digital Delivery Platforms: Use of FTP (File Transfer Protocol) or dedicated file-sharing platforms to send content to broadcasters, streaming platforms, or clients.
B. Encoding and Transcoding
Encoding for Distribution: Content must be encoded into various formats (H.264, H.265, etc.) suitable for different platforms and devices.
Transcoding: Converting files into multiple formats or bitrates to ensure compatibility and quality across different distribution channels.
C. Metadata Management
Metadata Creation: Adding metadata to media files for easier search and categorization (such as IDs, descriptions, and keywords).
Cataloging and Archiving: Systems for maintaining a digital archive of all assets, which can include cloud storage solutions.
D. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
Streaming Distribution: CDNs help distribute content efficiently across the internet, ensuring low latency and high availability for on-demand access.
3. Broadcasting
A. Broadcasting Technology
Transmission: Using digital broadcasting technologies (DTT, DAB, OTT) to transmit content. This includes managing signals for terrestrial, satellite, or cable broadcasting.
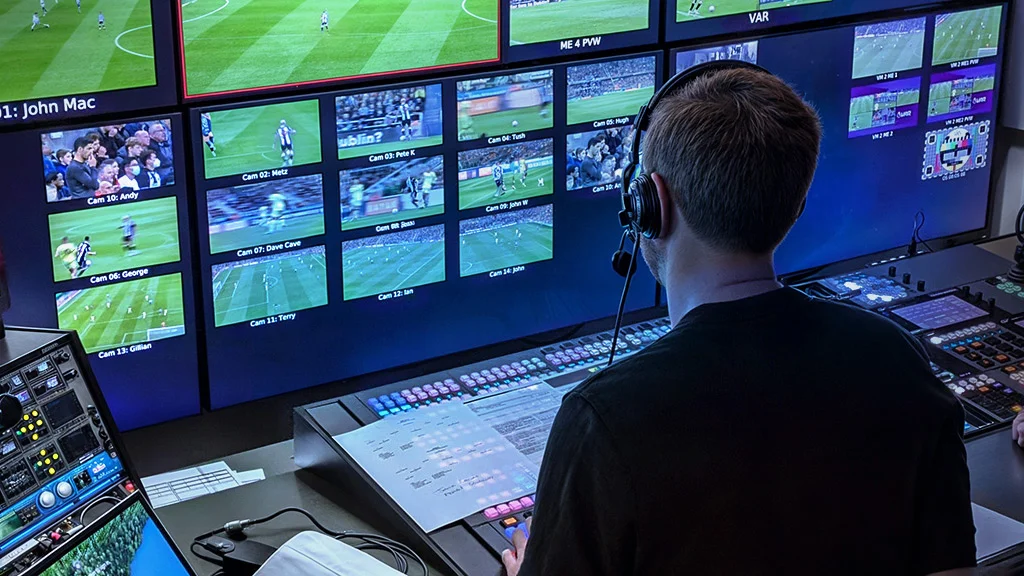
B. Live Broadcasting
Broadcast control room : Tools for broadcast control room , including players, audio and video mixers , video router modules etc.
Live Streaming Platforms: Tools for live broadcasting events, including software/hardware encoders and social media platforms.
C. Monitoring and Quality Assurance
Real-time Monitoring: Tools to monitor live broadcasts.
Broadcast live delay management : Tools to monitor Audio video delay management, ensuring signal integrity and compliance with broadcasting standards and guidelines.
User Experience Optimization: Technologies for analyzing viewer engagement, feedback, and streaming quality metrics.
D. Audience Interaction
Engagement Tools: Platforms for audience engagement during broadcasts (live polls, chat features), allowing for real-time interaction and feedback.
In summary, the digital workflow in broadcasting enhances collaboration, reduces costs, improves quality, and accelerates the delivery of content. By integrating modern digital technologies at every stage—from production through broadcasting—you can optimize your operations and better meet the demands of audiences in an increasingly competitive environment.
Read also :
Challenges in Broadcast Workflow Management
Broadcast workflow management involves coordinating a complex range of processes, technologies, and teams to deliver high-quality content efficiently. Despite advancements in technology, the sector faces several significant challenges that impact workflow efficiency and overall production quality.
1. Complexity of Multi-Platform Delivery
As audiences consume content across diverse platforms, broadcasters must adapt workflows to accommodate various formats, resolutions, and broadcast standards. This requires a seamless integration of multiple distribution channels, complicating the workflow and increasing the likelihood of errors.
2. Legacy Systems Integration
Many broadcast operations still rely on legacy systems that are not fully compatible with modern technologies. Integrating these outdated systems with new tools can lead to inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and increased operational costs, making it challenging to streamline workflows.
3. Real-Time Collaboration
Effective collaboration among diverse teams – from content creators to editors and engineers – is crucial for timely broadcasts. However, coordinating efforts in real time can be difficult, especially in remote or hybrid work environments. This challenge can hinder creativity and slow down the overall production process.
4. Content Management and Asset Organization
With the vast amount of content generated daily, organizing and managing assets become increasingly difficult. Ensuring that team members can easily access the right files and information at the right time is essential for maintaining workflow efficiency.
5. Quality Control and Compliance
Maintaining high-quality standards and meeting regulatory compliance can be challenging in a fast-paced broadcast environment. Implementing consistent quality control measures throughout the workflow is vital to avoid costly mistakes and ensure regulatory adherence.
6. Technological Adaptation
The swift progression of technology brings a twofold challenge. Broadcasters must continuously adopt new tools and technologies to remain competitive while ensuring that their teams are adequately trained to use them effectively. Balancing innovation with staff capability can strain resources.
7. Data Security and Privacy Concerns
As broadcast workflows become increasingly digital and interconnected, safeguarding sensitive data becomes very important. Managing cybersecurity risks while ensuring smooth operations is a delicate balance that must be prioritized.
8. Resource Allocation and Budgeting
Efficiently allocating resources and managing budgets can be particularly challenging in an industry subject to fluctuating revenues and audience demands. Striking the right balance between cost control and maintaining high-quality production values requires careful planning and foresight.

Future Trends in Broadcast Workflow Solutions
The broadcast industry is entering a transformative phase, driven by technological advancements, evolving viewer preferences, and the need for greater efficiency. Several key trends will shape broadcast workflow solutions, enhancing the ways in which the content is produced, distributed, and consumed.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are set to revolutionize production processes. in broadcasting, AI can automate routine tasks such as editing, tagging, and quality control, thereby significantly reducing production timelines. Additionally, AI-driven analytics will facilitate content personalization, providing viewers with tailored recommendations that enhance engagement.
- As the industry transitions to IP-Based Workflows, broadcasters will benefit from greater flexibility and interoperability. The shift from traditional SDI to IP networking allows for cost-effective scalability and simplified integration across different systems, enhancing overall operational effectiveness.
- Data-Driven Decision Making will become integral to broadcast strategies. Advanced analytics will offer insights into viewer behavior and content performance, allowing broadcasters to adapt their offerings in real time. By utilizing real-time metrics, teams can fine-tune content strategies to maximize audience engagement and drive profitability.
- The incorporation of Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR) into broadcast workflows will create new dimensions in storytelling. These technologies will not only enhance viewer experiences but also revolutionize live broadcasting through remote virtual production techniques, significantly reducing production costs and logistical challenges.
- In response to the diverse landscape of media consumption, broadcasters will adopt Diversity in Content Distribution strategies. This includes producing content tailored for various platforms, such as social media or OTT services while exploring innovative monetization models that blend subscription and ad-supported models.
- User-Friendly Interfaces and Training will be important in facilitating the adoption of new technologies. The Future of broadcast workflow solutions will prioritize intuitive designs that minimize the learning curve, supported by comprehensive training resources to keep teams abreast of advancements in the field.
The future of broadcast workflow solutions is destined to be more efficient, collaborative, and adaptable, driven by cutting-edge technology and an emphasis on sustainability. As broadcasters embrace these trends, they will not only enhance operational effectiveness but also elevate viewer engagement and content quality in an increasingly competitive market.